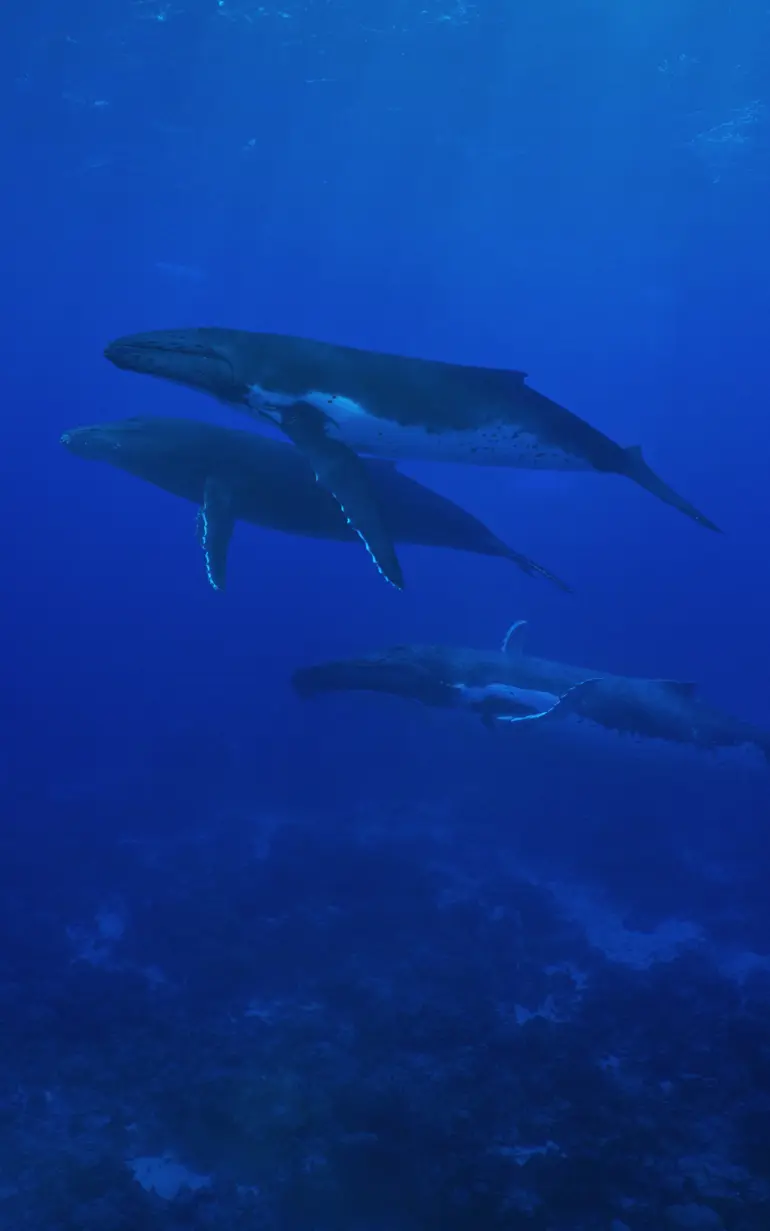


ABM Lab
Understand how aquatic disturbances affect habitat connectivity, migration, and populations
ABM Lab is advanced agent-based modelling software that simulates aquatic life to help understand the impact of disturbances. Dive into simulations within customisable environments, where users create virtual agents with unique attributes and behaviors, and explore how their interactions drive system-wide behaviors and emergent patterns.
Model everything from marine animal migration to the dispersal of coral larvae, all within a dynamic framework that adapts to both living and inanimate agents. ABM Lab's user-friendly interface and powerful modelling tools make experimentation, hypothesis testing, and policy evaluation accessible to researchers, policymakers, and analysts alike. Uncover insights, test scenarios, and make informed decisions with ABM Lab.
How does ABM Lab help?
No in-house modellers?
Get our expert modellers on board for your consulting projects either as a partner, to provide extended user support, or for model and project reviews. Submit an inquiry
Areas of application

Aquaculture planning & design
Boost aquaculture productivity by simulating the spread of waterborne diseases and parasites to refine prevention and treatment.

Climate change resilience and impact
Model adaptive behaviors of migratory aquatic animals to changing climates for informed adaptation strategies.

Contaminant fate and transport
Simulate contaminant movement through ecosystems, including potential impacts from invasive species via ballast water.

Ecological restoration projects
Develop effective restoration strategies by modelling interactions among organisms and environmental changes.

Environmental Impact Assessments
Assess offshore construction impacts on migratory aquatic animals using agent-based modelling to improve environmental compliance.

Eutrophication mitigation strategies
Simulate nutrient cycles and organism responses in protected areas to devise targeted eutrophication mitigation.

Flood impact assessments
Model ecological responses to flooding, considering impacts on migratory fish affected by hydropower.

Forecasting and early warning systems
Use agent-based models to predict ecological changes and issue early warnings, focusing on invasive species risks from ballast water.

Habitat response assessments
Analyse species and habitat responses to environmental stressors to enhance protection of marine protected areas.

Marine debris predictions
Predict debris movement in aquatic environments to align cleanup strategies with marine species protection.

Offshore planning, design, and construction
Simulate construction impacts on aquatic animal migration to minimise environmental disruption.

Oil spill modelling & emergency response
Model biological responses to oil spills, including impacts on marine protected areas.

Ship navigation planning support
Model interactions between shipping and marine life to manage ballast water and prevent invasive species spread.

Underwater noise impact assessments
Predict underwater noise impacts from offshore activities on marine life, guiding mitigation strategies for species protection.
Additional capabilities & unique features
Explore our latest support resources, including guides, videos, and FAQs in our Knowledge Base.
Experience faster MIKE ABM Lab FM simulation speed and useful new functionalities
With the release of MIKE 2023, MIKE ABM Lab users can now perform agent-based modelling calculations on dry elements. In addition, MIKE ABM Lab has been equipped with MPI parallelisation for enhanced performance when calculating ‘distance to shore’ and ‘direction to shore’.
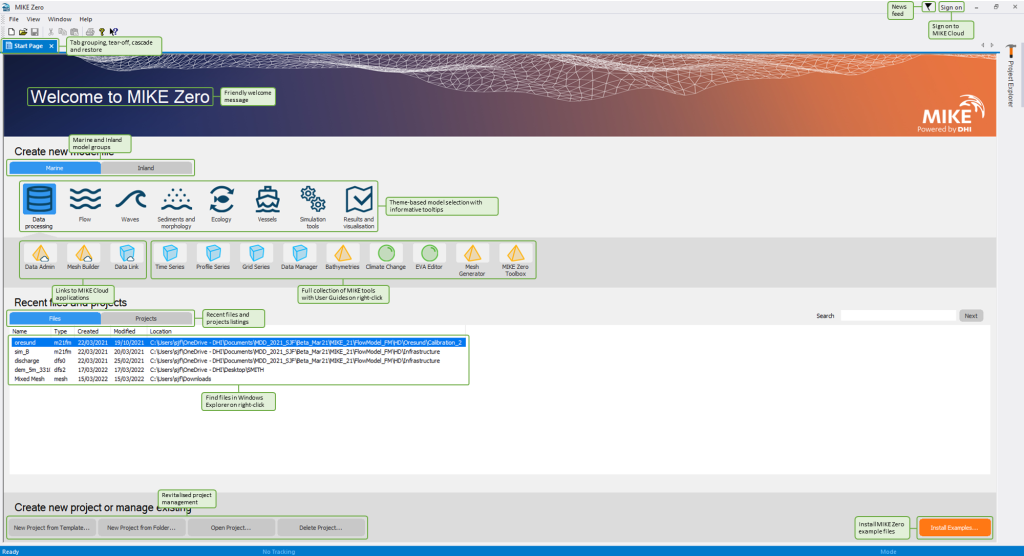
Get more done in less time with the modernised MIKE Zero user interface
Save time and improve your modelling workflows using MIKE Zero’s upgraded editors and viewers. Take advantage of new keyboard shortcuts and themes, improved tabbing, tear off and cascade functionality plus easier access to User Guides and Scientific Documentation.
New built-in constants and forcings for MIKE 21/3 FM
Rely on several new built-in constants with FM-based engine support. For example, users can now compute the approximate distance and direction to shore.
New algorithm for RASF computation in ABM Lab for MIKE 21/3 FM
Compute Remote Area Search Functions (RASFs) for concentration-based variables using an enhanced algorithm. Experience improved performance depending on the computational mesh size and search radius.
Access new tools, Cloud applications and an enhanced graphical overview from the redesigned MIKE Zero start page
MIKE Zero, DHI’s fully Windows integrated graphical user interface, is now better than ever and comes standard with all MIKE 21/3 software. Enjoy easy access to new MIKE Cloud applications and Cloud-enhanced functionality, plus an extended set of MIKE tools within theme-based (rather than product-based) interactive workflows. Ensure important model components such as sources and structures stay at the forefront with a new interactive, customisable floating mapping window. Lastly, the updated tabbing functionality will help you work in a more organised and efficient manner.
Available on Azure Marketplace
You can now access ABM Lab on Azure Marketplace, where you can start modelling in the cloud with no hardware limitation in four simple steps. Learn more
Create a real-time operational forecast system
Using MIKE OPERATIONS as the platform, ABM Lab can form the core of a new generation of risk assessment tools. For example, DHI recently created GlobalSEA SAR (Search and Rescue), an online operational system designed to mitigate risks of vessel grounding. The real-time integrated model predicts the vectors and speeds of vessels that have lost power or steerage to assess associated risks (e.g. grounding on a reef) and then proposes measures to abate it.
Conduct advanced Environmental Impact Assessments for aquatic organisms
ABM Lab offers advanced solutions to Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) for aquatic organisms – whether it involves the behaviour of large animals such as mammals and fish or dispersal units like larvae, seeds and spores of aquatic organisms. For example, users can model the response of large animals to disturbances like underwater noise from drilling or seismic surveys taking into consideration seasonal migrations as well as meteorological and hydrodynamic changes.
Model coral reef connectivity and impacts on mass coral spawning
Using ABM Lab, it’s possible to determine the connectivity between protected marine areas and define the importance of the protected area networks. For example, models of coral larvae dispersal can be developed, simulating mortality, larvae settlement, individual reaction to environmental and anthropogenic, gradients. Important connectivity corridors between coral reefs can then be identified based on these models.
Formulate new agent-based models in MIKE ECO Lab Templates
The built-in MIKE ECO Lab Template Editor is an efficient tool to formulate new agent-based models in MIKE ECO Lab templates, which can then be coupled to the hydrodynamic modules, MIKE 21 and MIKE 3 Flow Model FM.
Benefit from parallelisation to run fast simulations on systems with many cores
The computational engines of the MIKE 21/3 FM series are available in versions that have been parallelised using both shared memory as well as distributed memory architecture. The latter approach allows for domain decomposition. The result is much faster simulations on systems with many cores. It could be feasible to carry out ABM modelling using decoupled result files from a HD simulation.
Let's get started
Learn how your project can benefit from the powerful insight gained from agent-based modelling.
You may also like
How can we help?
With our global network of offices, we make sure you get the right answers to your local needs. Tell us about your water challenges and we will get back to you.






